Patient Access to Information PAC
The purpose of this page is to provide a better clarification on the specification of the implementation of the Patien Access Service on the OpenNCP scope.
To discuss this page please use the following issue:
PT-178 - Getting issue details... STATUS______________________________
PAC Service Implementation Overall Status
1. Scenarios Clarification
Goals
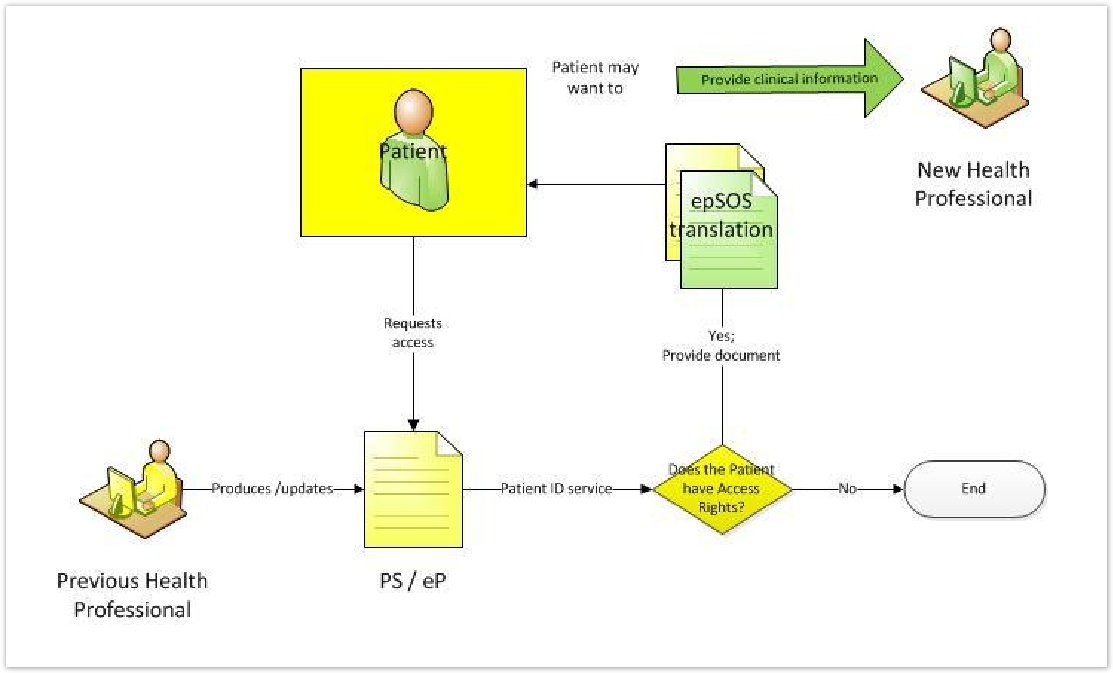
The goals of the main actor, the patient, in UC.PAC.1 is to access and understand what the Health Professional has recorded in the PS or eP, in order to:
- Participate in his or her own care, and/or to improve the information he or she gives to a New Health Professional;
Actors
The actors involved in the epSOS PAC Use Case are:
Primary actors:
- The Patient;
Secondary actors:
- The Health Professional, acting as a Healthcare Provider, producing the medical information used in the document to be accessed;
- The Health Professional at a new encounter (New Health Professional);
- Patient identification, authentication & role authorization service;
- The epSOS Patient Access translation service;
Diagram 1: Use case diagram
2. Requirements
Actions & Steps
| Steps | Actions |
|---|---|
| 1 | (This step is in the National Domain, and is a prerequisite for the PAC service)
|
| 2 | The Patient requests an epSOS translation of the retrieved document |
| 3 | The National Patient Access system passes the request to the epSOS NCP in Country A |
| 4 | The epSOS NCP in Country A provides a dialogue for selecting the source and target language (Language A, Language B) |
| 5 | The National Patient Access system sends the document (in Language A) to the epSOS NCP in Country A |
| 6 | The NCP-A transforms (transcodes) the document indicated (or received) from Patient Access system into a translatable epSOS pivot document and then makes this pivot document available to the translation responsible. |
| 7 | The translation responsible retrieves the epSOS MTC of Language B |
| 8 | The translation responsible translates the pivot document and makes the translated document in language B available to the NCP of country A |
| 9 | The NCP of country A conveys the information translated into the interface of the National Patient Access system |
| 10 | The patient accesses the translated document in his specific device display |
| 11 | The use case is finished/closed
|
Basic Service Functional Requirements
| FR01 | Patient Access Basic Requirement |
|---|---|
| Description | The Patient must have the possibility to access his/her own medical information available at his/her national PA service ( affiliation’s country) and get it translated into any epSOS country language Specific PA services asks first its NCP-A for PS/eP translation service. As a consequence NCP-A requests a translation. Each translation request to an NCP-A must include these parameters 1. Affiliation country where the Patient has identified/authenticated himself |
| Associated Goals |
|
| Actors | 1. Patient |
| Preconditions |
|
| FR02 | Patient identification and authentication: a univocal digital ID |
|---|---|
| Description | epSOS Patient Access (PAC) must be in accordance with the Patient Access policy of patient’s Country of Affiliation [9]. Access by the patient to epSOS related functionalities through its National Patient Access shall not interfere with this rule. The patient will be univocally identified in a reliable way (unique and unequivocal id) to consult his information. Patient authentication will be guaranteed at national level based on the concept of mutual trust. |
| Associated Goals |
|
| Actors | 1. Patient |
| Preconditions |
|
| FR03 | Trust between countries |
|---|---|
| Description | Country A and B are integrated on one circle of trust (technical and functional). It’s necessary an agreed framework for creating trust, by establishing policies, processes and procedures for critical data protection, privacy and confidentiality issues as well as mechanisms for their audit. Such issues include, but are not limited to:
|
| Associated Goals |
|
| Actors |
|
| FR04 | Request from country A for a document translation |
|---|---|
| Description | For any provided epSOS pivot content in structured form (both CDA level 1 and level 3), Country A requests the translation of all coded elements that are used to describe the epSOS data set. Country A has to provide original data in epSOS CDA compliant form, i.e. the friendly document that has exactly the form of epSOS pivot document, (Ref.: in Specs of common components p.19) |
| Associated Goals | none |
| Actors |
|
| FR05 | Patient identification and authentication: a univocal digital ID |
|---|---|
| Description |
|
| Associated Goals |
|
| Actors |
|
| FR06 | Information Traceability |
|---|---|
| Description |
|
| Associated Goals |
|
| Actors |
|
| FR07 | Peering both original documents and translations |
|---|---|
| Description | Patient and healthcare professional must be able to consult a copy of the original document (with no epSOS semantic transformation) and the translated document. |
| Associated Goals | none |
| Actors |
|
| Preconditions |
|
| FR08 | Consultation of PoC through the patient access service - OPTIONAL |
|---|---|
| Description | For this service the steps in the country National Domain are the same as above for eP/PS. For the realm of epSOS the National Patient Access system retrieves the PoC through the NCP or from the epSOS website. |
The patient must be able to consult available PoC in the area where he is interested in for any type of health care providers (e.g. hospitals, healthcare centers and pharmacies). It is a Browsing function returning the list of all PoC in the specified territory value set. The patient triggers the event; the requested Point of Care in an area is the origin of the event; the Service consumer is NCP that triggered the event | |
| Associated Goals |
|
| Actors |
|
| Preconditions |
|
Service Legal Requirements
For service legal requirements please consult the D 1.4.3, page 112;
Service Security Requirements
For service security requirements please consult the D 1.4.3, page 114;
Service Clinical Requirements
For service clinical requirements please consult the D 1.4.3, page 115.
Service Usability and Data Presentation Requirements
For service usability and data presentation requirements please consult the D 1.4.3, page 117.
Additional Architecture NCP / Central Service requirements
For additional Architecture NCP / Central Service requirements please consult the D 1.4.3, page 122.
3. Clarification
The purpose of this topic is to clarify some remaining questions and doubts about the Patient Access specification of OpenNCP.
- Can the service workflow be accomplished using the NCP-B + Portal-B?
4. Implementation Strategy Design
4.1. Overview
Multiple ways can be followed in order to implement the Patient Access service on the OpenNCP. The most direct one is to make use of existent components and implemented services. Others will require further development.
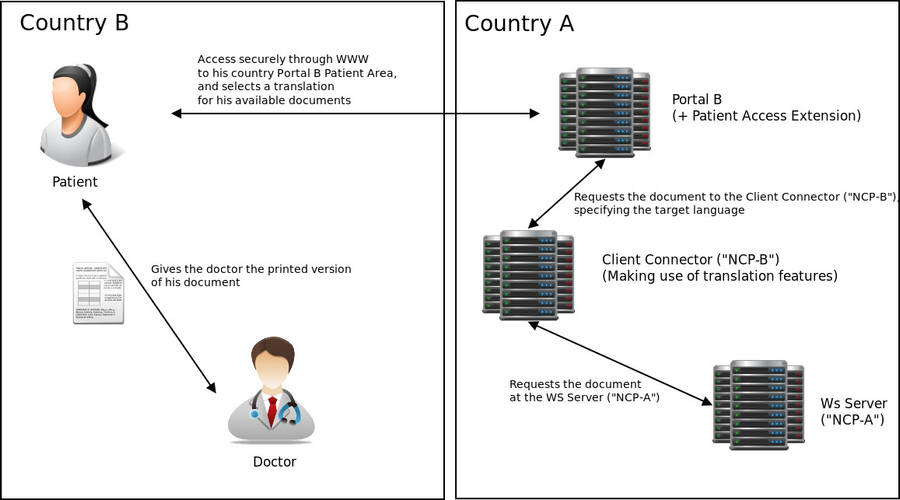
4.2. Solution A: Re-use the Portal-B + NCP-B as Patient Access and Translation Service
Basic solution diagram
In order to promote the maximum components re-use we can define the following table to map the required PAC service elements into the existent OpenNCP components:
Mapping table of Patient Access Elements into OpenNCP components
| Patient Access Required Element | OpenNCP Existent Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Country-A Patient Access Service | Portal-B with Patient Access Section + NCP-B | As a default implementation, the Patient Access service can be provided by the existent Portal solution for OpenNCP. It will be necessary to implement a Patient Section. |
| Translation Service | NCP-B (In patient country of affiliation) | The translation service can be provided by the NCP-B of the country of affiliation, since it will support the target language selection |
| NCP-A | NCP-A (In patient country of affiliation) | The NCP-A can be used as it is, with no further modification. |
We can also map the required steps into the following OpenNCP actions and operations:
Mapping table of required steps into components actions and operations
| Steps | Actions | OpenNCP actions and operations description | To be implemented in OpenNCP | Related Profiles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (This step is in the National Domain, and is a prerequisite for the PAC service)
|
| A Portal-B Patient Section, with the following aspects:
| XCPD, XCA |
| 2 | The Patient requests an epSOS translation of the retrieved document |
| (Described further bellow) | |
| 3 | The National Patient Access system passes the request to the epSOS NCP in Country A |
| ||
| 4 | The epSOS NCP in Country A provides a dialogue for selecting the source and target language (Language A, Language B) |
| Target language selection for translating a document at the Portal-B patient section;
| |
| 5 | The National Patient Access system sends the document (in Language A) to the epSOS NCP in Country A |
| Already supported; | XCA |
| 6 | The NCP-A transforms (transcodes) the document indicated (or received) from Patient Access system into a translatable epSOS pivot document and then makes this pivot document available to the translation responsible. |
| Already supported; | XCA |
| 7 | The translation responsible retrieves the epSOS MTC of Language B |
| Already supported by TM; | |
| 8 | The translation responsible translates the pivot document and makes the translated document in language B available to the NCP of country A |
| Adapt Client Connector to support language specification when retrieving a document;
| XCA |
| 9 | The NCP of country A conveys the information translated into the interface of the National Patient Access system |
| Already supported; | XCA |
| 10 | The patient accesses the translated document in his specific device display |
| Adapt portal to support multiple XSLT for each language; Possibly add PDF production feature (for easier portability and printing); | |
| 11 | The use case is finished/closed
|
Implementation Mapping with existent Workflows
Assumptions - Example
- Country B is Greece;
- Country A is Italy;
Existing Portal-B workflow | PAC Workflow |
|---|---|
Pharmacist accesses Greek Portal-B | Italian Patient accesses Italian Portal-B |
1. hcp asserion | 1. hcp asserion (needs to be specified new role and permissions for patient). I am not sure if patient is an HCP (healthcare point) |
2. identification service (finds an Italian patient) | 2. identification service (the system automaitically identifies itself, the patient stores to the portal the personal identifiers needed for matching with the patient) |
3. TRC Assertion | 3. TRC Assertion (the system automatically creates a trca with purpose of treatment, new role has to be defined) |
4. patient service | 4. patient service (the system automatically retrieves list of documents) |
5. Consent handling if needed | 5. Retrieval and display of document (translation of document not needed, it's in italian language already, no transformation needed) |
6. Retrieval of document (translation of document in country b language - greek in this occasion) | 6. Consent handling must be part of ncp-a in order to allow patient to see its own data |
Questions
- Does it needed a new audit event for this transaction?
So if the patient role had permissions on patient service he could probably see his documents
Implementation Issues / Tasks:
Portal-B
Protocol Terminators
Transformation Manager / TSAM / TSAM-Sync
Considerations
- In this scenario we will re-use all the existent components to meet the PAC Service requirements;
- Some security issues need to be taken into account, in order to restrict the retrieval of "patient-only" documents;
4.3. Solution B: Newly create Patient Access and Translation Service components
In this option we would need to expose an additional service for translation purposes only at NCP-A, skipping the re-use of NCP-B.
(To be completed if required)
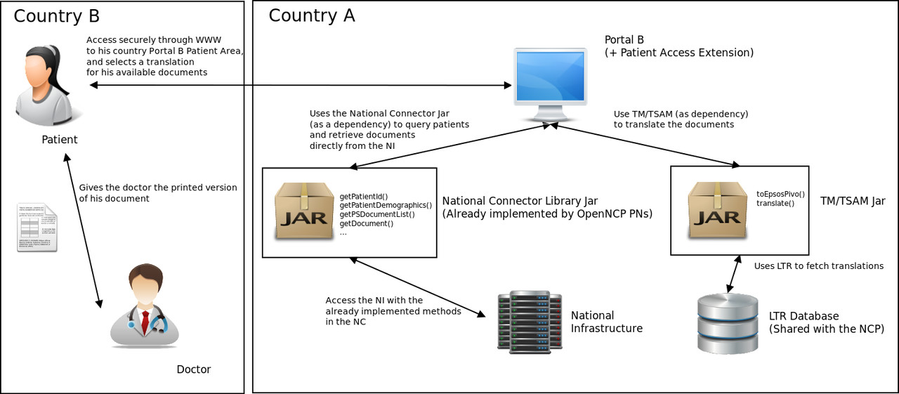
4.4. Solution C: Use Transformation Manager and National Connector library as Portal dependencies
With this solution we would have the Portal communicating directly with the National Infrastructure, using the already implemented National Connector (by the OpenNCP PNs). The translation would be performed by the Transformation Manager, added also directly as a dependency of the Portal.
The following diagram tries to explain the proposed solution.
Basic solution diagram (click to enlarge)
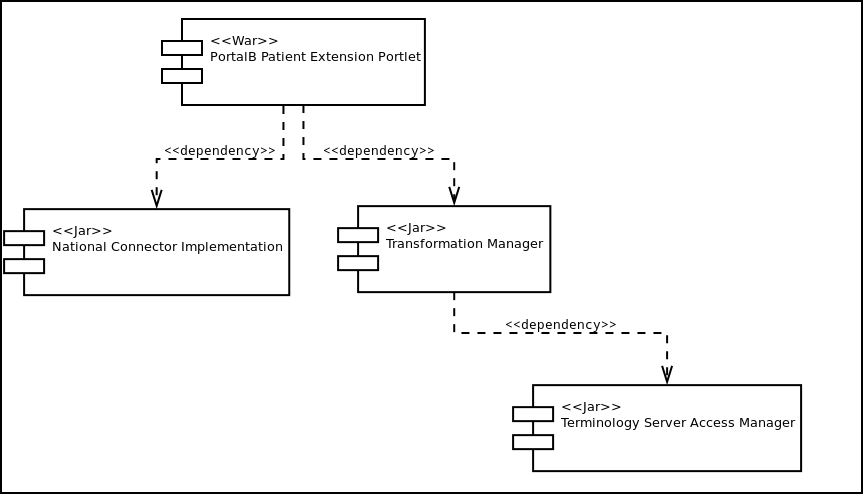
In order to clarify the portal dependencies, the following diagram is presented:
Portal dependency graph
Mapping table of required steps into components actions and operations
| Steps | Actions | Portal actions and operations description | To be implemented in the Portal | Related Profiles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (This step is in the National Domain, and is a prerequisite for the PAC service)
|
| A Portal-B Patient Section, with the following aspects:
| NI specific |
| 2 | The Patient requests an epSOS translation of the retrieved document |
| (Described further bellow) | |
| 3 | The National Patient Access system passes the request to the epSOS NCP in Country A |
| ||
| 4 | The epSOS NCP in Country A provides a dialogue for selecting the source and target language (Language A, Language B) |
| Target language selection for translating a document at the Portal-B patient section;
| |
| 5 | The National Patient Access system sends the document (in Language A) to the epSOS NCP in Country A |
| ||
| 6 | The NCP-A transforms (transcodes) the document indicated (or received) from Patient Access system into a translatable epSOS pivot document and then makes this pivot document available to the translation responsible. |
| The Transformation Manager toEpsosPivot() invocation; | |
| 7 | The translation responsible retrieves the epSOS MTC of Language B |
| Already supported by TM; | |
| 8 | The translation responsible translates the pivot document and makes the translated document in language B available to the NCP of country A |
| The Transformation Manager translate() invocation; | |
| 9 | The NCP of country A conveys the information translated into the interface of the National Patient Access system |
| ||
| 10 | The patient accesses the translated document in his specific device display |
| Adapt portal to support multiple XSLT for each language; Possibly add PDF production feature (for easier portability and printing); | |
| 11 | The use case is finished/closed
|
5. Test Strategy Design
(To be defined after strategy validation)
6. References